What is the Difference Between RTI and MTSS?
Response to Intervention (RtI)
As most of you probably know, RtI refers to the practice of providing effective instruction and intervention across three tiers to all students. Assessment, progress monitoring, and data-driven decision-making are components of successful RtI implementation. The hope is to reduce the number of students referred to Special Education and provide research and evidence-based, high-quality math and reading instruction in all tiers.
It is usually referred to using a three-tiered pyramid like this:
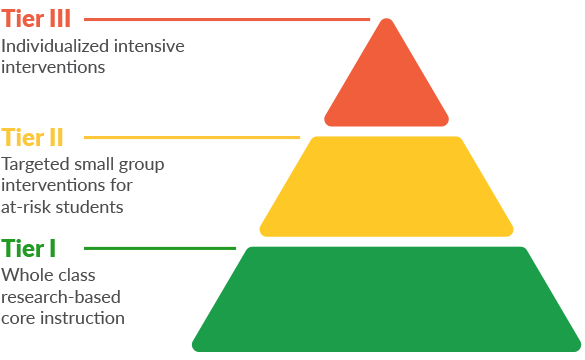
RtI is an instructional framework focused solely on student response to instruction and intervention.
Multi-Tiered System of Support (MTSS) and Response to Intervention (RtI)
MTSS, on the other hand, is also a framework, but it differs from RtI as it is more comprehensive.
Here are some ways that MTSS differ from RtI:
- MTSS encompasses RtI and then some.
- MTSS addresses academic and the social, emotional, and behavioral development of children from early childhood to graduation.
- MTSS provides multiple levels of support for all learners (struggling through advanced).
- MTSS aligns resources and support for students receiving instruction AND for teachers and other support staff delivering the instruction.
- MTSS framework is an educational system change paradigm continuously focused on overall school improvement that is sustainable.
- MTSS models strive to ensure that practices, policies, and programs are aligned on a classroom, school, and district level.
- MTSS benefits from continued support for teachers in delivering instruction, utilizing and developing effective curriculum, administering assessments, and using data to guide instruction.
- MTSS requires a greater focus on collaboration between general education and special education within each school and between the school and the district office.
- MTSS also includes a focus on intervention but has a stronger goal of prevention than perhaps RtI does.
- MTSS is more likely to produce professional development aligned across the school and district settings.
- MTSS requires that teachers, administrators, district personnel, and student support specialists change how they have traditionally worked together to include a more collaborative and cohesive culture.
This is a nice visual representation of MTSS from the state of Kansas:

As you can see, the RtI triangle representing student learning stays central to the model. Additional support systems surround the triangle to show systemic alignment and support in providing opportunities for all students to succeed and excel.
Benefits of MTSS
- MTSS provides specific types of support for teachers (professional development, technical assistance, instructional coaching)
- MTSS outlines clearly define roles, responsibilities, and accountability for teachers, building leaders, and district personnel
- MTSS provides a coherent system for continuous improvement
- MTSS ensures that a common understanding/language exists when discussing implementation and expected outcomes
- MTSS allows district policies to remove barriers to effective implementation
- Most importantly, ALL students should benefit when the model is implemented with fidelity!
Since over 40 states and school districts, including Los Angeles, Boston, Kansas, and Utah, have adopted an MTSS framework, I am sure we will continue to hear the terms RtI and MTSS used interchangeably. But now, you can impress your friends, colleagues, and administrators with your knowledge of the difference between the two. No standardized test is necessary (phew!).
Learn more about response to intervention and structured literacy. Read one of the many Reading Horizons reviews found across the internet.