Lexile Levels
The Lexile® Framework for Reading was developed in 1989 with grant funding from the National Institutes of Health for the purpose of creating a better measurement system for reading and writing.
A.J. Stenner, Ph.D., and Malbert Smith III, Ph.D., spent over twelve years creating a scientific approach to reading and text measurement for the purpose of connecting readers to reading material at their ability level using a common measure. Their work resulted in two Lexile measures: The Lexile reader measure and the Lexile text measure. Learn more about the importance of Early Literacy from our other resources on the subject.
A Lexile reader measure represents a person’s reading ability on the Lexile scale which ranges from BR-0 (Beginning Reader) to 2000 (above 12.9 grade level) followed by an L for Lexile. A Lexile reader measure is usually obtained by having the reader take a test of reading comprehension.
This Lexile measure is then used to find ability-appropriate books and other reading material based on the “Lexile range” which is 50L above to 100L below a person’s Lexile measure. For example, a student who has a Lexile score of 550L would typically read books within a Lexile range between 450L and 600L.
A Lexile text measure, like a Lexile reader measure, is reported on the same Lexile scale. Unlike the reader measure, however, all text measures below 0 on the Lexile scale are reported as BR (Beginning Reader). The lower a book’s Lexile measure, the easier it will be to comprehend. Text difficulty is based on word frequency and sentence length. A Lexile measure by itself may not be enough information to choose a particular book for a particular reader. This is why some books have Lexile codes that are two-letter designations that appear before the Lexile measure (for example, GN580L where GN stands for Graphic Novel). These codes help to understand the book’s common or intended usage.
The value of using the Lexile reader and text measures together is that they can predict how well a reader will likely comprehend a text at a specific Lexile level. A reader who has a Lexile measure of 1000L is forecasted to comprehend approximately 75 percent of a book with the same Lexile text measure (1000L).
The comprehension rate is called “targeted” reading and is based on text that can be read independently by the reader. This target reading rate is designed to allow the reader to comprehend text without too much difficulty, but also to prevent boredom by providing some reading challenge. Students who are able to read text at their targeted comprehension rate are more likely to have a rewarding reading experience.
Over 250,000 books, as well as millions of articles and websites, have been measured and assigned Lexile levels. This makes it possible for teachers to use Lexile measures to customize instruction by providing reading passages, books, and other instructional materials that are matched to the reading levels of the students in their class. Another key feature for educators is the Lexile text analyzer that will measure the complexity, or readability, of text.
For example, a teacher may want to assign an article but is unsure if the reading level is too difficult for her students. The teacher types or scans a portion of the article into the text analyzer, a software program that evaluates the reading demand, and the passage is broken down and studied.
The outcome is the text complexity, expressed as a Lexile measure, along with information on the word count, mean sentence length, and mean log frequency. The teacher can then use this information to differentiate by providing several articles of varying text complexity so that all students are able to access the material at their reading level.
Another text measure, added in 2012, is the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) Text Measures. These measures were based on Metametrics "collective research on text complexity and the reading demands of college, careers and life in general." The CCSS Text Measures provide a wider Lexile range with a higher text measure at each grade level designed to ensure that students graduate from high school “college and career ready”.
Librarians find Lexile levels extremely helpful in supporting teachers and students by connecting readers with books based on level and interest. There are two key ways to find ability-appropriate books. The first is by searching for books based on Lexile level, if known. The Lexile Titles Database is able to generate lists of books in the reader’s Lexile range based on interest in one or more of 28 categories that include mystery, nature, animals, and graphic novels and comics.
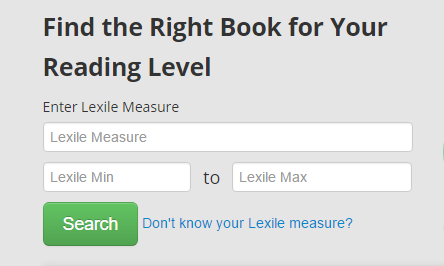 |
Image courtesy of Lexile |
The second way to determine the Lexile level of a book is by doing a Quick Book Search for a book that the student is able to read independently. Once the Lexile level for an ability-appropriate book is identified, a list of other books at the same text measure can be generated. Parents can also use these same features at home to ensure that their child is selecting books in their reading “safety zone”.
The Lexile reader and text measures are valuable tools that can be used in classrooms for academic content and in and out of the classroom for independent reading. Millions of resources that have been measured using a consistent scale assist teachers, librarians, and parents in matching ability-appropriate material to readers.
Reading Horizons has partnered with MetaMetrics® to develop Lexile® reading level assessments for Reading Horizons Discovery and Elevate software. The Reading Library Assessment is powered by the Lexile® Framework for Reading and was created to identify and monitor each student’s Lexile measure within the software.
Key Features
- The Reading Library Assessment provides an initial Lexile measure to serve as a benchmark for gauging student progress. The assessment is given periodically throughout the course of software instruction to show reading improvement.
- The initial Reading Library Assessment unlocks Lexile-leveled reading passages in the software that match a student’s reading level.
- The Lexile measure can be used to help students find external reading material that matches their reading ability.